motherboard chipset- these are blocks of microcircuits (literally a chip set, that is, a set of chips) responsible for the operation of all other computer components. It also affects the performance and speed of the PC.
As you understand, in addition, close attention should be paid to the chipset placed on it, especially when it comes to modern powerful home or gaming computers.
It is easy to identify them visually on the motherboard - these are large black microcircuits, which are sometimes covered with cooling radiators.
In the already outdated scheme for constructing a motherboard, the chipset microcircuits were divided into two blocks - the north and south bridges according to their location on the diagram.
The functions of the north bridge are to ensure the operation of the processor with RAM (RAM controller) and video card (PCI-E x16 controller). The southern one is responsible for communicating the processor with other computer devices - hard drives, optical drives, expansion cards, etc. via SATA, IDE, PCI-E x1, PCI, USB, sound controllers.
The main performance characteristic of the chipset in this architecture is the data bus (System Bus), designed to exchange information between various parts of the computer. All components work with the chipset through buses, each at its own speed. This is clearly seen in the chipset diagram.
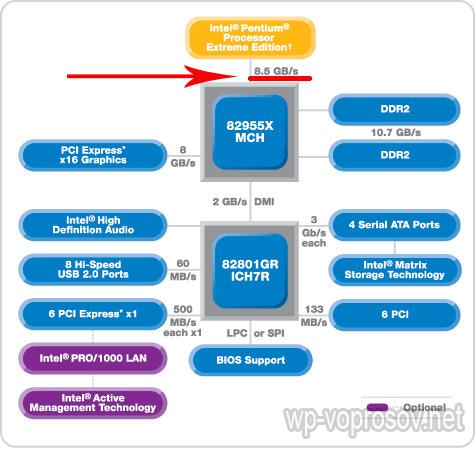
The performance of the entire PC depends precisely on the speed of the bus that connects it with the chipset itself. In the terminology of Intel chipsets, this bus is referred to as FSB (Front Side Bus).
In the description of the motherboard, it is referred to as the "bus frequency" or "bus bandwidth".
Let's take a closer look at these characteristics of the data bus. It is determined by two indicators - frequency and width.
- Frequency- This is the data transfer rate, which is measured in megahertz (MHz, MHz) or gigahertz (GHz, GHz). The higher this indicator, the higher the performance of the entire system as a whole (for example, 3 GHz).
- Width- the number of bytes that the bus has the ability to transfer at a time in bytes (for example, 2 byte). The larger the width, the more information the bus can transmit in a certain period of time.
When multiplying these two values, we get the third one, which is exactly indicated on the diagrams - throughput, which is measured in gigabytes per second (Gb / s, Gb / s). From our example, we multiply 3 GHz by 2 Bytes and get 6 Gb / s.
In the picture below, the bus bandwidth is 8.5 gigabytes per second.
The northbridge is connected to the RAM using a dual-channel controller built into it via the RAM Bus, which has 128 pins (x128). When working with memory in single-channel mode, only 64 tracks are used, so for maximum performance it is recommended to use 2 memory modules connected to different channels.
Architecture without northbridge
In the latest generation of processors, the northbridge is already built into the chip of the processor itself, which significantly increases its performance. Therefore, it is completely absent on new motherboards - only the south bridge remains.
In the example below, the chipset does not have a northbridge, since its function is taken over by a processor with an integrated video core, but from it we also see the designation of the data bus speed.
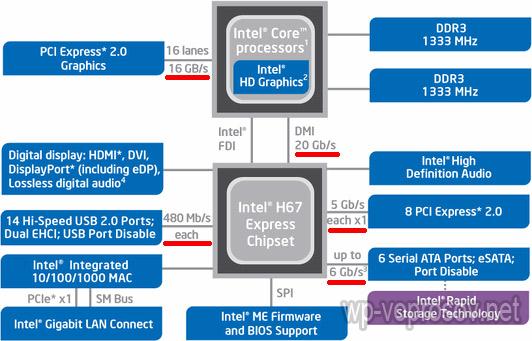
Modern processors use the QPI (QuickPath Interconnect) bus, as well as the PCI-e x16 graphics controller, which used to be in the north bridge, and is now integrated into the processor. As a result of being embedded, the performance of the main data bus is not as important as it was in the previous generation dual-bridge architecture.
In modern chipsets on new boards, there is another bus operation parameter - transfers per second, which indicates the number of data transfer operations per second. For example, 3200 MT/s (megatransfers per second) or 3.2 GT/s (gigatransfers).
The same characteristic is indicated in the descriptions of processors. Moreover, if the chipset has a bus speed of 3.2 GT / s, and the processor, for example, 2 GT / s, then this bundle will work at a lower value.
Chipset manufacturers
The main players in the market of chipset manufacturers are already familiar to us from Intel and AMD, as well as NVidea, which is better known to users for its video cards, and Asus.
Since the first two are the main manufacturers today, let's take a look at modern and already outdated models.
Intel chipsets
Modern- 8x, 7x and 6x series.
Obsolete- 5x, 4x and 3x, as well as NVidea.
The chipset marking with a letter in front of the number means the power of the chipset within one line.
- X- maximum performance for gaming computers
- R— high performance for powerful computers of mass application
- G- for a regular home or office computer
- B, Q- for business. The characteristics are the same as "G", but have additional features, such as remote maintenance and access monitoring for administrators of large offices and enterprises.
Recently, several new series have been introduced for the new LGA 1155 chipset:
- H- for ordinary users
- R 67— for enthusiasts who plan further upgrades and overclocking of the system
- Z- universal option, combines the characteristics of the two previous ones
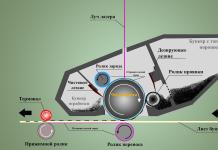
From the chipset diagram, you can easily understand what built-in and external functions it supports. For example, let's look at the scheme of a modern productive Intel Z77 chipset.
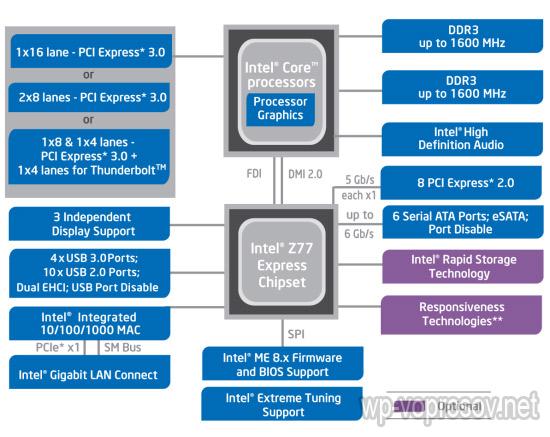
The first thing that attracts attention is the absence of the north bridge. As we can see, this chipset works with processors with integrated graphics core (Processor Graphics) of the Intel Core series. For a home computer, the built-in kernel will be enough to work with documents and watch videos. However, if you need more performance, for example, when installing modern games, then the chipset supports the installation of several video cards in the PCI Express 3 slot. Moreover, when installing 1 video card, it will use 16 lines, two - each with 8 lines, or one 8, the other 4 , and the remaining 4 lines will be used to work with devices using Thunderbolt technology.
The chipset is also ready for further upgrades and overclocking (Intel Extreme Tuning Support).
For comparison, let's look at another chipset - Intel P67, which is pictured below. Its main difference from the Z77 is that it does not support the built-in video core of the processor.
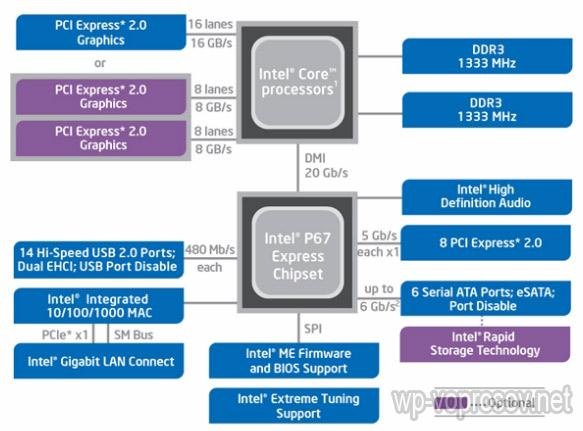
This means that a motherboard equipped with the P67 will not be able to work with the integrated graphics core of the processor and you will definitely need to buy a discrete (separate) video card for it.
AMD Chipsets
Modern- Axx series (for processors with an integrated video core), 9xx and 8xx.
Obsolete- 7xx, nForce and GeForce, except for some models.
The weakest in performance are those models in the name of which there are only numbers.
- Letters G or V in the model name indicates the presence of an integrated video card in the chipset.
- X or GX- support for two separate (discrete) video cards, but not at full capacity (8 lines for each).
- FX are the most powerful chipsets that fully support multiple graphics cards.
The bus that links the processor and chipset from AMD is called Hyper Transport (HT). In modern chipsets that work with AM2+, AM3, AM3+ sockets, it is version 3.0, in AM2 it is 2.0.
- HT2.0: max frequency - 1400 MHz, width 4 bytes, bandwidth 2.8 GT / s
- HT3.0: max frequency 2600 MHz, width 4 bytes, bandwidth 5.3 GT/s
Let's look at an example of a motherboard description on the site and determine which chipset is placed on it.
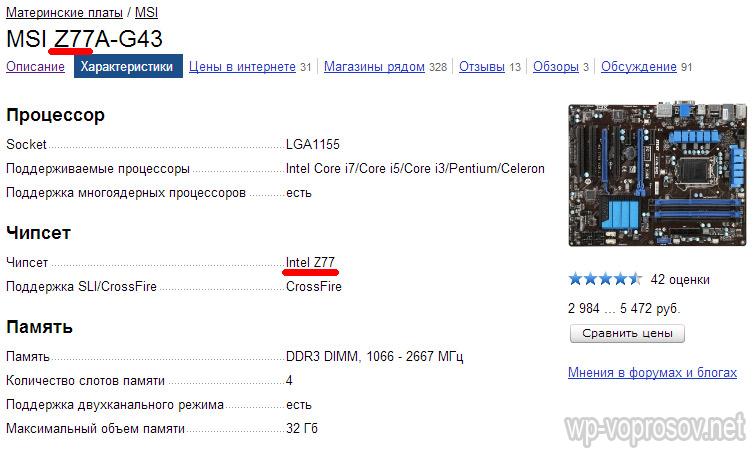
In this figure, we have the MSI Z77A-G43 model - it is already clear from the name itself that it is equipped with the Intel Z77 chipset, which is also confirmed in the detailed description.
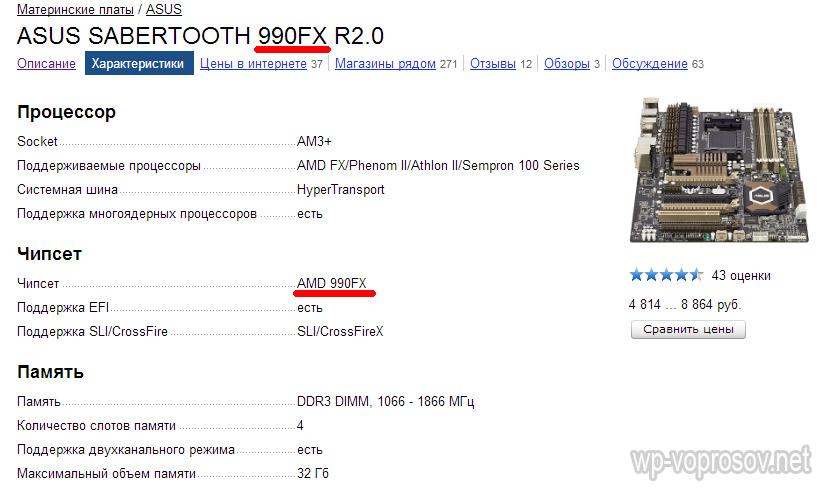
And here is the ASUS SABERTOOTH 990FX R2.0 board with a productive chipset from AMD 990FX, which is also evident both from the name and the detailed description.
What is the best motherboard chipset?
Let's summarize - what is the best chipset to choose for your computer?
It all depends on what purpose you are building your PC for. If this is an office computer or a home computer on which you do not plan to install games, then it is advisable to choose a chipset that works with processors with an integrated graphics core. By purchasing such a board and, accordingly, a processor with built-in video, you will receive a kit that is quite suitable for working with documents and even watching videos in good quality.
If you need more in-depth work with graphics, for example for average video games or graphics applications, then you will use a separate video card, which means there is no point in overpaying for a graphics chipset that supports work with an integrated video processor - it is better if it provides maximum performance video cards.
For the most powerful gaming PCs, and to a lesser extent those that will run graphics-intensive professional software, choose the highest performing models that fully support multiple graphics cards.
I hope this article has opened a little for you the veil on the mystery of motherboard chipsets and now you can more correctly choose these components for your computer! Well, to consolidate knowledge, watch the video tutorial posted at the beginning of the article.